Agentic Workflows: A Guide for Marketers
Published on October 31, 2025/Last edited on October 31, 2025/10 min read


Team Braze
Most marketing workflows still rely on pre-set rules and static branching, which makes them fragile when customers behave differently than expected. When this happens, personalizing beyond broad segments quickly becomes unmanageable.
Agentic workflows solve this by putting adaptive AI agents inside the journey itself. These agents do more than follow instructions—they make decisions in real time, test alternatives, and learn from outcomes. This results in cross-channel journeys that scale without losing relevance, and campaigns that improve with every send.
Contents
What are agentic AI workflows?
Real-life agentic workflows in marketing
Framework for AI workflow orchestration
Agentic workflows vs. AI decisioning vs. next-best action
Build vs. buy: where data platforms end and orchestration begins
Challenges of agentic workflows
Final thoughts on agentic workflows
What are agentic AI workflows?
Agentic workflows are AI-powered systems that weave autonomous agents into the flow of customer engagement. Instead of relying on rigid “if-this-then-that” logic, they continuously experiment, adapt, and refine decisions—choosing the right message, channel, or timing for each individual in the moment.
It’s the difference between a scripted sequence that always follows certain rules and logic, versus a dynamic system that can handle complexity, test alternatives, and adjust on the fly. Agentic AI workflows let brands evolve along with their customers and with every interaction.
How agentic workflows operate
Agentic workflows function by bringing together several moving parts into a single system:
- Context: customer profiles, behavioral events, and real-time signals that shape decisions.
- Agents: autonomous decision-makers that analyze inputs, plan actions, and adapt.
- Tools and integrations: APIs, data sources, and external systems that agents use to act.
- Orchestration layer: the flow that connects channels and coordinates tasks across the customer journey.
- Feedback loop: reinforcement learning and experimentation that allow the system to improve over time.
Autonomous workflows: adapting in real time
Some workflows can run with a single AI agent acting independently. These autonomous workflows use live context—such as customer behavior or engagement history—to decide when to send a message, which channel to use, or what content to deliver. Because the agent can perceive, plan, act, and learn without human intervention, the workflow adapts dynamically instead of following rigid rules.
Multi-agent workflows: collaborating for complexity
Multi-agent workflows are a type of autonomous workflow designed for more complex processes. Here, several AI agents take on different tasks—such as analyzing context, selecting the channel, or applying guardrails—but work together toward a shared goal. If one element changes, all agents coordinate and adjust, using context to create the next best action, deliver the most relevant message, and choose the right channel. This makes it possible to run 1:1 real-time personalization at scale, across even the most intricate journeys.
Guardrails are essential across both autonomous and multi-agent workflows. They define eligibility, frequency caps, compliance constraints, and approval thresholds. With the right controls in place, marketers gain workflows that adapt dynamically while staying safe, consistent, and trustworthy.
Real-life agentic workflows in marketing
Agentic AI workflows are most valuable when they turn adaptive decision-making into measurable results. Here are a few examples marketers can act on today:
- Boost engagement with adaptive timing and channel choice: Agents analyze individual behavior to decide when and where to reach each person, improving open and click-through rates.
- Protect margins while increasing conversions: An “Offer Agent” tailors discounts or content in real time, while guardrails make sure incentives stay within brand and compliance limits.
- Reduce onboarding drop-offs: Journeys flex to each user’s adoption path, nudging them toward key actions when they stall.
- Capture relevance in the moment: Location, weather, or live events trigger context-specific messages that feel timely and personal.
To see the impact more clearly, let’s look at how brands are applying these workflows today. The case studies below illustrate the role of agentic workflows in boosting onboarding performance and driving long-term value.
Grubhub’s onboarding upgrade delivers 836% ROI
Grubhub, part of Just Eat Takeaway, partners with 365,000+ restaurants across 4,000 US cities. Their Campus program brings tailored dining experiences to students at more than 300 colleges.
Challenge
Student adoption of Grubhub Campus was low. Many began the onboarding process but dropped off before completing critical steps like linking a campus card or activating their Grubhub+ Student subscription.
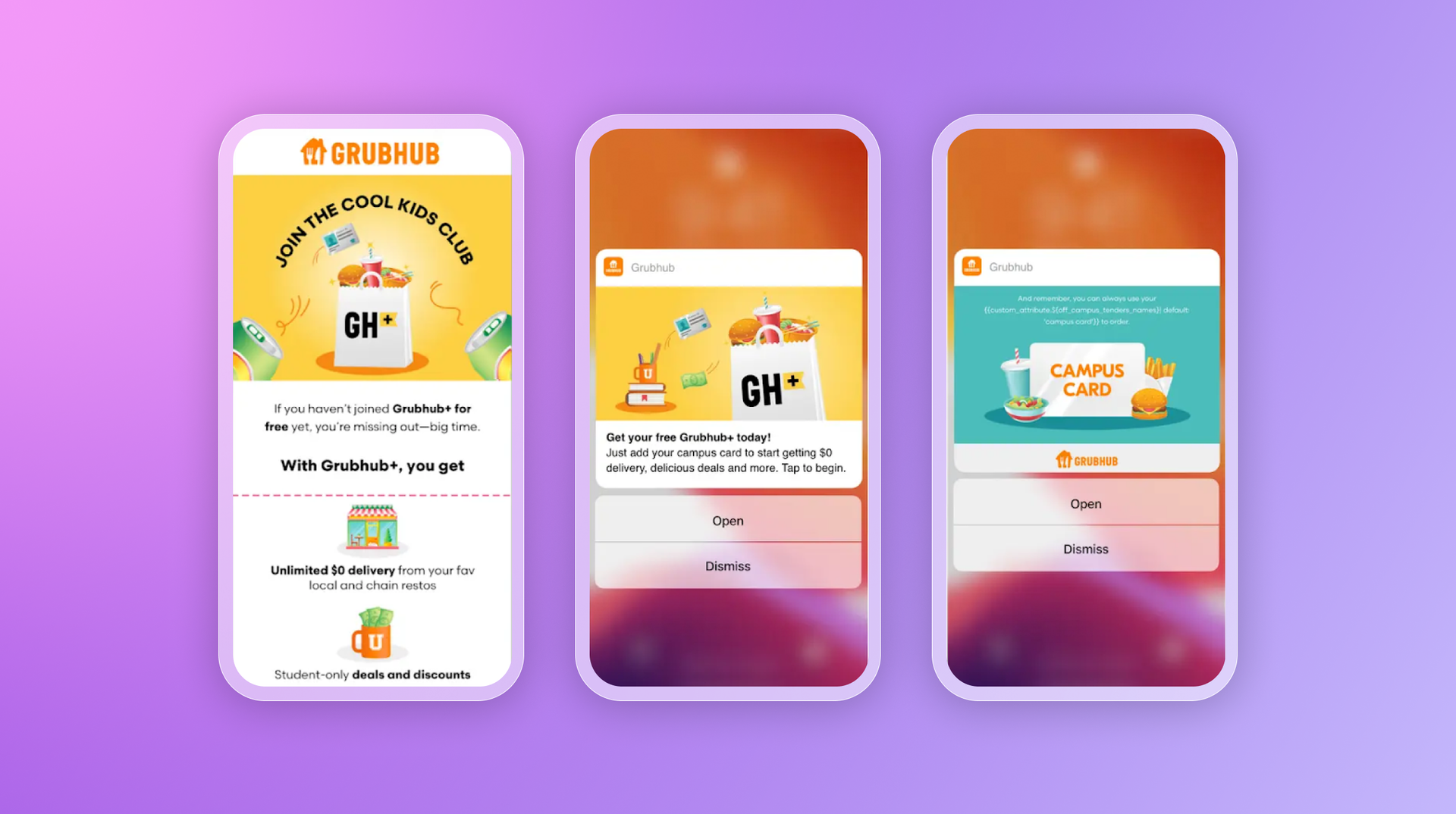
Solution
Using Braze Canvas, Grubhub designed a multi-stage onboarding journey with personalized emails and push notifications. Each stage had a clear goal—from welcoming new students, to prompting campus card verification, to nudging Grubhub+ activation. With Braze Alloys integrations (Amplitude, Google Analytics), the team tracked engagement and optimized flows in real time.
Results
The results speak for themselves:
- 836% increase in return on investment (ROI)
- 20% more orders overall
- 188% rise in Grubhub+ Student signups
By shifting from static welcomes to adaptive, agent-like orchestration, Grubhub educated students at each step and kept them moving forward—showing how onboarding journeys built with agentic workflows can drive adoption, loyalty, and measurable revenue impact.
foodora builds trust and drives engagement through BrazeAI™
foodora is a leading food delivery service operating in over 700 cities across Europe. Their mission is to deliver convenience and joy by giving people access to what they want, when they want it. To achieve this, foodora emphasizes strong customer relationships built on trust, timely communication, and personalized experiences.
The challenge
foodora struggled with inconsistent messaging across multiple platforms and lacked predictive insights to guide engagement. This resulted in missed opportunities, low engagement rates, and higher churn.
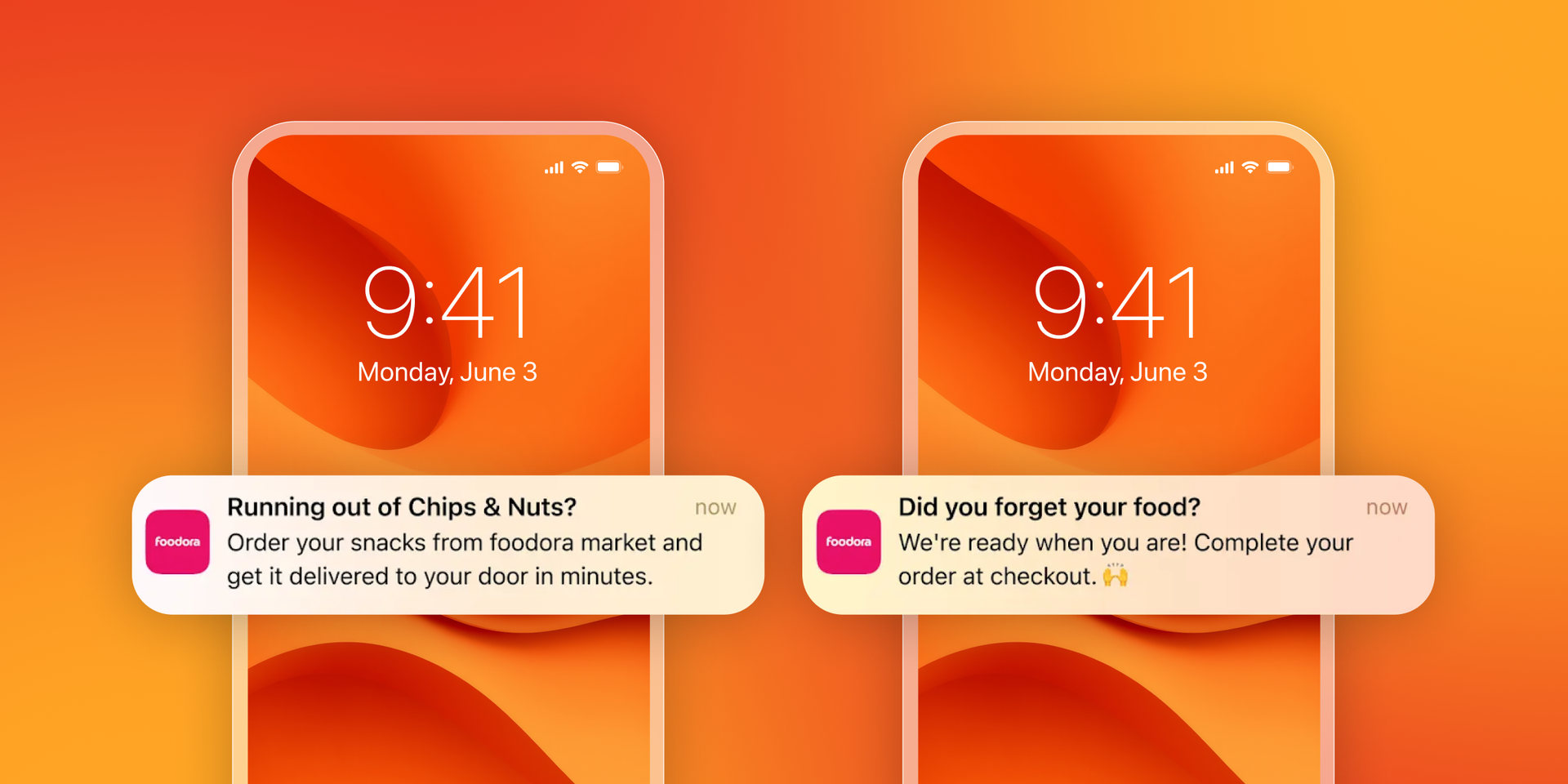
The solution
Switching to Braze allowed foodora to unify their customer engagement strategy across email, push, and in-app messaging. By adopting BrazeAI™ Intelligent Timing, they optimized message delivery to reach customers when they were most likely to engage. This personalized send-time approach reduced intrusiveness, boosted satisfaction, and strengthened trust.
The results:
- 41% conversion rate from messages sent
- 26% reduction in unsubscribe rate with Intelligent Timing
- 6% increase in push direct opens
foodora’s success highlights the impact of agentic workflows on customer engagement. By shifting from fixed schedules to AI-powered send-time optimization, they showed that when a message is delivered can be just as important as what it says.
Framework for AI workflow orchestration
Building an agentic workflow starts with clarity. Marketers can follow this step-by-step approach:
Define the objective and KPI
Decide what success looks like. For example, reduce churn by 10% or lift repeat purchases by 15%.
Map signals and data
Identify which behavioral, contextual, and consent signals agents will use to make decisions.
Choose agent decisions
Decide what the agents will control: channel, timing, content, and/or offer.
Set guardrails
Put in place constraints like frequency caps, brand tone rules, and compliance policies.
Orchestrate across channels
Use a journey flow (like Braze Canvas) to connect channels and sequence decisions.
Measure and learn
Establish a test cadence, track uplift, and feed results back into the workflow for continuous experimentation and improvement.
This framework helps marketers translate abstract AI concepts into a concrete plan they can design, test, and scale.
Agentic workflows vs. AI decisioning vs. next-best action
These terms may seem similar, but each method functions differently and leads to different personalization outcomes.
- Next-best action refers to personalization based on prediction models and finds the next best product, step, or recommendation based on segmented data. Customers within a defined segment will receive the most relevant message, offer, or response in real time.
- Agentic workflows can vary based on your personalization model. By embedding autonomous agents that perceive, plan, act, and learn, they string decisions together across an entire journey. Instead of making one-off predictions, the system adapts continuously—coordinating timing, channel, content, and offers as conditions change.
- AI decisioning uses reinforcement learning and autonomous AI agents to evaluate options—such as whether to send a discount, adjust timing, or switch channels—experiment, and continuously learn from results. AI decisioning executes sophisticated 1:1 personalization based on unique customer profiles and first-party data, and your business goals.
Build vs. buy: where data platforms end and orchestration begins
Some brands already have a Customer Data Platform (CDP) or data activation layer in place. These tools unify customer profiles and streaming events, but weren’t designed to orchestrate journeys in real time or personalize at scale.
CDPs and data tools handle the foundation: They centralize data and make it accessible across systems. Essential groundwork, but not enough to drive adaptive, 1:1 engagement.
Orchestration and decisioning layers turn data into action: This is where marketers can design adaptive workflows, set business goals, and let AI agents personalize timing, content, and channels in the moment.
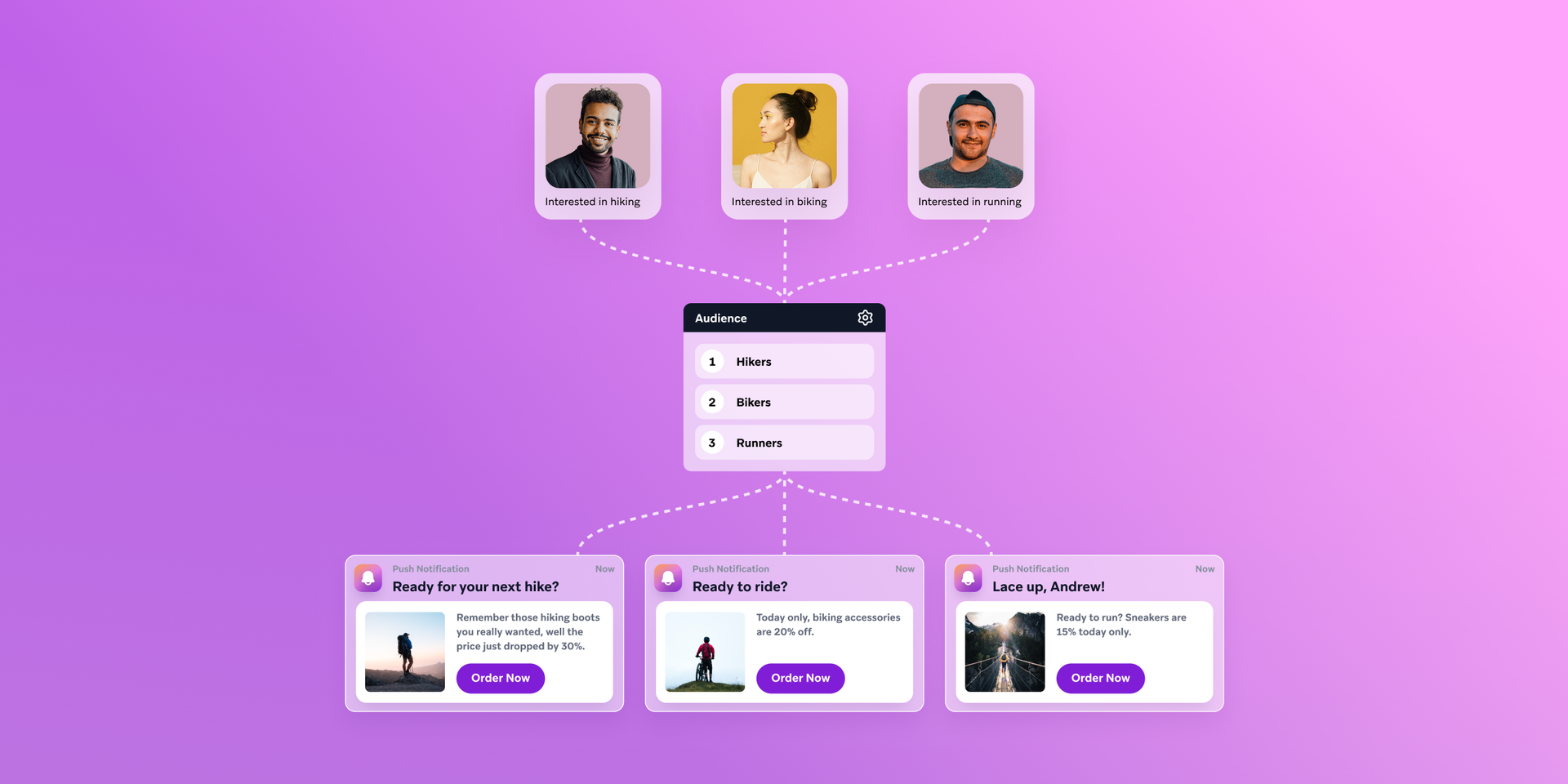
Teams face a choice in how to approach this:
- Build in-house: Develop custom agents and orchestration logic on top of the data layer. This offers flexibility but demands heavy engineering resources and can slow time to market.
- Adopt a platform: Choose a system with orchestration and AI decisioning already embedded—one that slots into the existing tech stack, scales with growth, and gives more control to the marketing team.
Challenges of agentic workflows
Agentic workflows only deliver value when they can be trusted. The same qualities that make them powerful—autonomy, adaptability, and scale—also create new risks for marketers. Unlike rules-based automation, agents can make independent decisions and adapt in real time, which means oversight, compliance, and brand safety become more complex.
Some of the key challenges include:
Transparency and explainability: Agentic workflows using machine learning models can make some decisions difficult to trace; there can be issues with reliability or unpredictable behavior that marketers need to keep an eye on.
Bias and fairness: Agents learn from data. If that data reflects historical bias, it can lead to skewed or unfair outcomes. Guardrails and ethical testing help prevent amplification of these issues.
Compliance and consent: Regulations and customer expectations around privacy evolve quickly. Agentic workflows must respect consent flags, preference centers, and regional data laws in every decision.
System integrity: Because agents connect with APIs and external tools, brands need strong access controls and authentication to keep interactions consistent, safe, and aligned with best practices.
Human oversight: While agents can act autonomously, certain decisions—like eligibility for an offer or frequency of outreach—may need human approval or preview before execution.
Ways to address these risks include sandbox testing before deployment, human-in-the-loop review options, audit trails, and deterministic fallbacks that default to approved actions if the agent cannot resolve a decision. Together, these measures create governance that balances speed and autonomy with safety and accountability.
Final thoughts on agentic workflows
Agentic workflows make personalization a living process—they are always learning, adapting, and relevant. They close the gap between strategy and execution by embedding decision-making directly into the journey itself. Supported by Braze, brands can operationalize this approach and create customer experiences that keep up with change and thrive on it.
Agentic workflow FAQs
What are agentic workflows?
Agentic workflows are adaptive systems where AI agents make real-time decisions inside a marketing journey. They adjust steps as customer behavior changes, keeping campaigns relevant at scale.
How do agentic workflows differ from traditional automation?
Agentic workflows differ from traditional automation because they don’t follow fixed paths. Instead, they experiment, learn from feedback, and adapt continuously.
How do agentic AI agents work inside a marketing workflow?
Agentic AI agents in a workflow process customer signals, decide on the next action, and refine future steps based on results.
What are examples of agentic workflows in marketing?
Examples of agentic workflows in marketing include adaptive onboarding, churn-reduction journeys, personalized send-time optimization, and contextual promotions.
How do agentic workflows improve personalization at scale?
Agentic workflows improve personalization at scale by analyzing each user’s context and tailoring content, timing, and channel automatically.
What KPIs should marketers use to evaluate agentic workflows?
Marketers can evaluate agentic workflows using KPIs like conversion lift, churn reduction, lifetime value impact, opt-out rates, and decision speed.
How do Braze and AI decisioning support agentic workflows?
Braze supports agentic workflows through real-time orchestration, AI decisioning, and guardrails that let agents personalize safely across channels.
What guardrails and governance are needed?
Guardrails in agentic workflows include consent checks, frequency caps, approval modes, audit trails, and fallback rules.
How do agentic workflows improve marketing outcomes?
Agentic workflows improve marketing outcomes by making campaigns faster to adapt, more relevant to individuals, and more efficient in spend.
How do multi-agent workflows work in marketing?
Multi-agent workflows use specialized agents—for audience selection, offer choice, channel, and guardrails—that collaborate to deliver coordinated experiences.
Releated Content
View the Blog
Braze vs Salesforce: Which customer engagement platform is right for your business?

Team Braze

Braze vs Adobe: Which customer engagement platform is right for your brand?

Team Braze

Every journey needs the right (Canvas) Context
